皮革科学与工程 ›› 2019, Vol. 29 ›› Issue (04): 5-9.doi: 10.19677/j.issn.1004-7964.2019.04.001
• 试验研究 • 下一篇
水解酶及硝化菌剂强化处理制革废水的研究
马宏瑞,王慧琴,朱超,周建军
- 陕西科技大学环境科学与工程学院,陕西 西安 710021
Study on Hydrolytic Enzyme and Nitrifying Bacteria Agents Enhanced Treatment of Tannery Wastewater
MA Hongrui,WANG Huiqin,ZHU Chao,ZHOU Jianjun
- School of Environmental Science and Engineering, Shaanxi University of Science &Technology, Xi’an 710021, China
摘要:
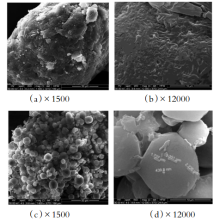
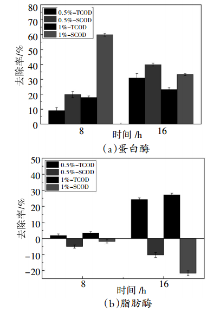
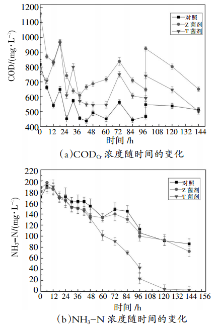
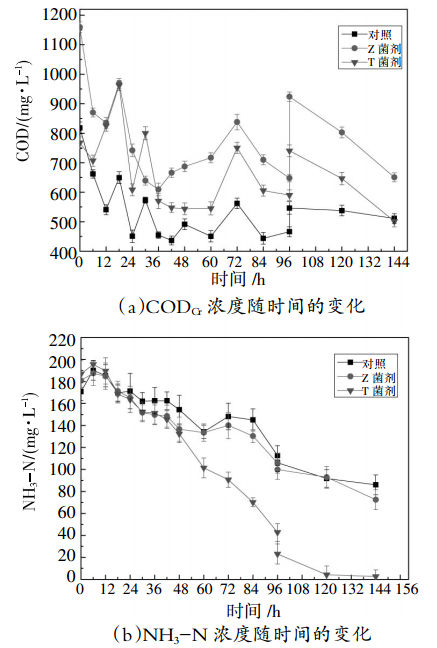
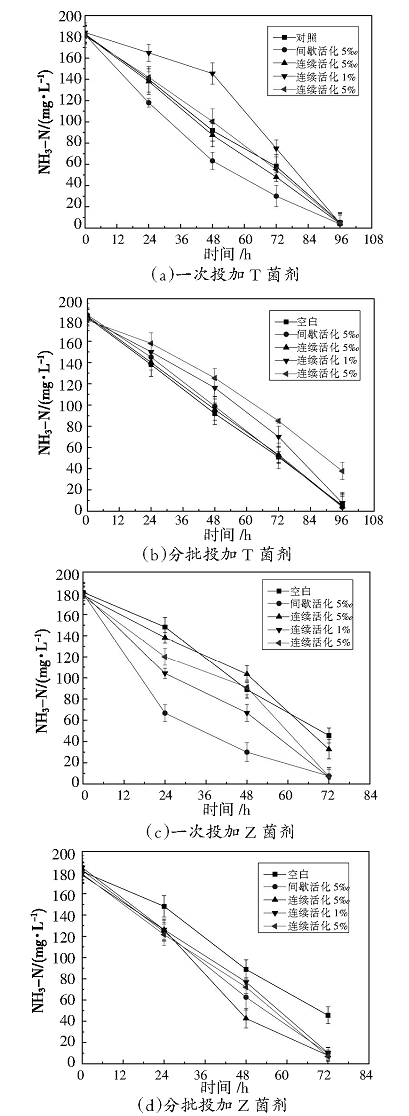
针对制革废水高悬浮物、高油脂、高总氮、高氨氮的特点,通过在传统A/O工艺的A段投加两种水解酶,在O段投加两种硝化菌剂实现制革废水的分段强化脱氮处理,并考察菌剂的不同活化以投加方式对脱氮效率的影响。结果表明,投加蛋白酶可有效去除高浓度制革综合废水中的TCOD、SCOD,投加脂肪酶可将高浓度制革综合废水中的悬浮物转化为溶解性物质,两种水解酶均可提高废水的可生化性。比较直投菌粉和经不同方案活化后的菌剂处理废水后发现,投加活化后的Z菌剂可在72 h实现氨氮的达标排放,去除率达96%,达标时间较直投菌粉时缩短了近50 h。对比两种菌剂在各自不同的活化及投加方式下对氨氮的强化去除效果后发现,它们之间的差异不大。
中图分类号: